Britain Cannot Tax & Spend Its Way Out of Its Economic Challenges & how AI can help with a brighter future
Publish Date: Last Updated: 10th February 2025
Author: nick smith- With the help of CHATGPT
The UK economy faces a substantial fiscal challenge, with an estimated £20–£40 billion deficit at the center of the nation’s economic discourse. Despite government assurances that recent measures aim to stabilize the economy, the underlying issues run deeper and require more than simple taxation. Britain needs systemic reform, focusing on cutting wasteful spending, reducing fraud, and employing efficient use of resources—not just new taxes—to address its pressing economic problems.
The Economic Burden
Since the last Conservative government, the UK's economy has encountered multiple obstacles, from Brexit to the fallout of Liz Truss’s brief term, during which the city was unprepared for her proposed economic changes, causing a short-term spike in interest rates. While subsequent fiscal policies stabilized the situation, the notion that Labour must "stabilize" the economy is arguably based on selective interpretation of facts.
The economic burden placed on UK citizens is significant, primarily through extensive taxation rather than targeted cost reductions. For example, the welfare state alone demands approximately £266.2 billion annually, divided among the 24.9 million people in employment. The NHS contributes an additional £180 billion to public expenses, while local council debt stands at £97.8 billion. The list of costs—from overseas aid to civil service expenditures and immigration controls—continues to grow, straining the public purse. Relying on increased taxation alone will not be sufficient to address these demands.
A Closer Look at Waste and Mismanagement
Examples of wasteful spending are prevalent. Recently, reports emerged of £100 million allocated to protect bats from HS2 trains, despite the improbability of these creatures colliding with high-speed trains due to their advanced echolocation abilities. Meanwhile, funding shortages prevent essential services, such as disability equipment for vulnerable people, which would require only a fraction of this amount. Such disparities in spending highlight the need for a complete overhaul of budget priorities.
In addition, the annual cost of fraud in the UK is estimated at £50 billion. Reducing fraud by even half would significantly alleviate the fiscal burden, potentially bridging the current deficit without increasing taxes.
The Housing Crisis: An Expensive, Self-Created Problem
The UK’s housing crisis costs approximately £26 billion annually, yet remains unsolved despite viable, affordable solutions. Prefabricated, modular housing units—available for as little as £30,000 per unit—could provide immediate relief, similar to the post-war housing solutions of the 1950s. Constructing compact communities using modern modular units could temporarily alleviate homelessness and reduce reliance on private landlords, while empowering local councils to reinvest in public services.
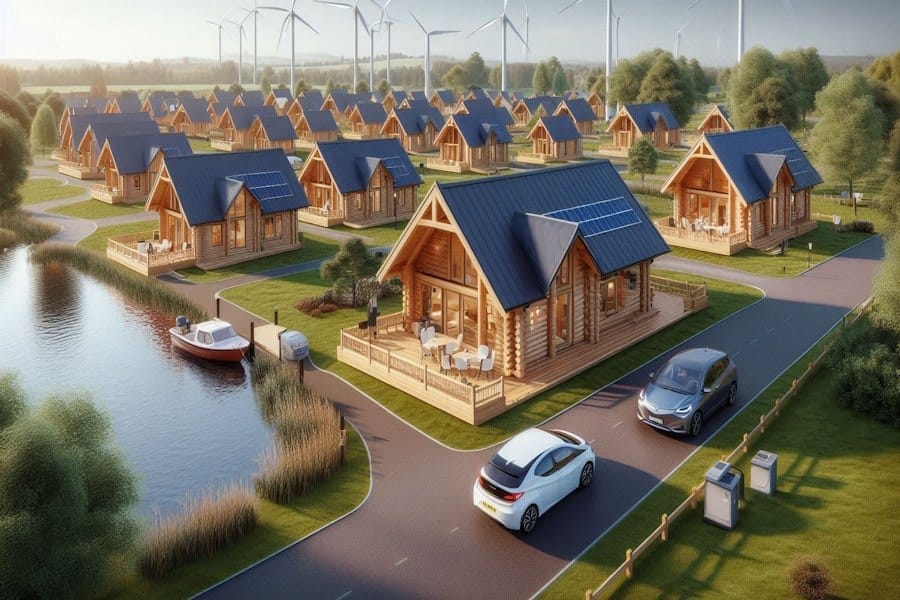

Would you rather be spending 3/4 of your salary to live in cramped accomodation or chose an alternative that costs only a 1/3 of your salary?
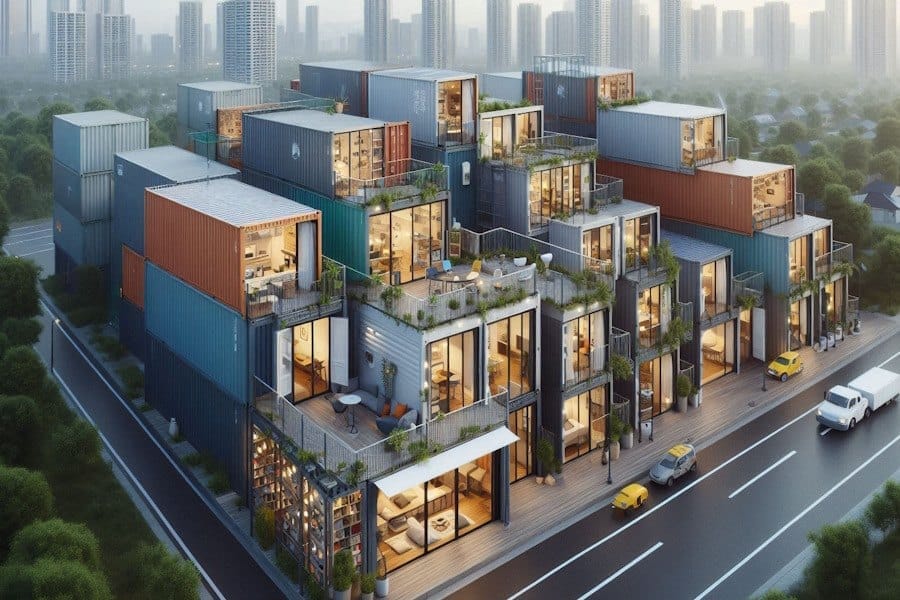

Shipping containers converted into affordable living units
Re-Evaluating Energy Policy: The Case for Carbon Capture
The UK’s approach to energy policy and climate commitments has also contributed to increased costs. Britain has access to significant coal reserves, estimated to last for a century. While environmental concerns halted coal use, modern carbon-capture technology could enable the safe use of this resource. Recent advances in carbon capture have reduced the cost to as low as $39 per metric ton, suggesting that decarbonized coal may offer a more economically viable alternative than nuclear energy. Hinkley Point C, for instance, is projected to cost £46 billion, with significant decommissioning and waste storage expenses exceeding £3 billion per year extending for at least 50 years at a high security storage facility followed by 100s of years of storage at 'less secure' untis.
A Call for Bold Solutions
The UK needs leaders willing to implement real, tangible changes, focusing on reducing fraud, cutting waste, and taking advantage of innovative, cost-effective solutions. Addressing the housing crisis through modern modular housing and exploring carbon-capture-enabled coal could help bridge economic gaps, generate jobs, and create more affordable living conditions.
Labour now has an opportunity to make meaningful changes over the next five years. However, early actions—marked by higher taxes and increased spending—indicate a familiar cycle of taxation-driven solutions. Britain’s economic problems are structural, not merely fiscal, and require targeted reforms, efficiency improvements, and a commitment to sustainable resource management.
If Britain is to achieve a brighter future, it must adopt a more strategic approach, prioritizing systemic reform over short-term financial fixes. This will lay the foundation for lasting growth, lower unemployment, and a more resilient economy for generations to come.
How AI Can Help the UK Government Make Savings and Cut Down on Fraud
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers unprecedented opportunities for the UK government to tackle inefficiencies, reduce fraud, and make intelligent spending decisions. With AI-powered tools and systems, the government can automate processes, analyze vast amounts of data, and implement fraud detection mechanisms that were previously impossible. Here’s a look at how AI can support these aims and help alleviate the UK’s economic burden.
1. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud costs the UK government around £50 billion annually, stretching public funds and placing additional burdens on taxpayers. AI can help cut this by identifying and preventing fraudulent activities across multiple domains.
Predictive Analytics
AI systems using predictive analytics can detect unusual spending patterns or behaviors in real-time. For instance, AI algorithms can monitor transactions to identify anomalies that might indicate fraud, such as duplicate claims or unusually large payments. This approach is already being used in sectors like banking and could be adapted to government finance systems to proactively flag suspicious activity.
Machine Learning Algorithms for Fraud Detection
Machine learning (ML) models trained on historical data can uncover complex fraud patterns that traditional systems may miss. For example, AI can analyze data across welfare, healthcare, and tax systems to detect connections between different types of fraud. By leveraging advanced ML algorithms, the government could develop a comprehensive fraud-detection system, allowing for quicker intervention and saving billions.
Identity Verification Systems
AI-powered biometric and facial recognition technology can play a crucial role in verifying identities for welfare claims, immigration processes, and other government services. Implementing biometric verification could help reduce fraud in benefits and other social programs, preventing cases where multiple claims are filed under a single identity or stolen identities are used to access funds.
2. Optimizing Public Spending
AI-driven systems can also identify areas of excessive spending and suggest efficiencies, reducing waste and freeing up resources for essential services.
AI-Enhanced Budget Analysis
AI can assess government budgets at a granular level, helping identify patterns and trends in public spending. This could be used to pinpoint areas where spending has consistently exceeded the necessary levels or where allocated funds are underutilized. For example, by using AI to analyze spending on NHS supplies, the government could identify opportunities to streamline procurement processes, reducing costs and improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Intelligent Automation in Public Services
Through robotic process automation (RPA) and natural language processing (NLP), AI can automate routine government processes, from processing applications to managing document verification. This can not only reduce labor costs but also improve service speed and reduce backlogs. The Department of Work and Pensions, for instance, could use RPA to automate benefit processing, allowing human employees to focus on complex cases while reducing administrative costs.
Dynamic Resource Allocation
AI algorithms can dynamically allocate resources where they’re most needed, particularly in sectors like healthcare and social services. For instance, predictive AI models could anticipate demand for medical supplies based on seasonal trends or public health data, helping reduce waste and ensure resources are always allocated where they’ll have the greatest impact.
3. Enhancing Tax Collection and Reducing Evasion
Tax evasion is a persistent issue, costing the UK billions each year. AI can improve tax collection by identifying discrepancies and automating certain enforcement processes.
Advanced Data Analysis for Tax Audits
AI systems can analyze financial data from various sources to detect tax discrepancies and identify cases for audit. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in financial data, AI can increase the accuracy and efficiency of tax audits, ensuring high-risk cases are identified faster. This can help HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) recover lost revenue while reducing the time and resources typically required for audits.
Real-Time Compliance Monitoring
AI can monitor transactions and financial activities in real-time, identifying suspicious transactions that may indicate tax evasion. For example, by analyzing real estate transactions, high-value purchases, or offshore account activity, AI can flag possible instances of tax avoidance and initiate further investigation. This proactive approach would enable HMRC to act swiftly and deter evasive practices before they escalate.
Automation of Routine Tax Collection Processes
AI-powered chatbots and automated systems can streamline routine tax-related queries and services, reducing administrative strain on HMRC. By automating repetitive tasks like tax calculations and document verification, AI allows human employees to focus on more complex cases, increasing efficiency and service quality.
4. Improving Policy-Making with Data-Driven Insights
AI can assist policymakers in making informed decisions based on data, ensuring policies are targeted, effective, and financially sound.
AI-Powered Policy Simulation Models
AI can create simulation models to predict the effects of potential policies on various sectors, from healthcare to housing. By analyzing historical data, these models can anticipate economic impacts, such as job creation or budget savings, and provide data-driven insights into which policies would yield the best outcomes.
Sentiment Analysis for Public Feedback
Sentiment analysis, powered by AI, can analyze public opinions on proposed policies and help gauge their likely acceptance. By evaluating social media, news articles, and public comments, AI can provide policymakers with real-time insights into public sentiment, enabling the development of policies that align more closely with citizens' needs and values.
Environmental Impact Analysis
AI can help assess the environmental impact of policies, such as new infrastructure projects, by simulating carbon footprints and resource demands. For example, AI could model the environmental impact of renewable energy projects versus traditional energy solutions, enabling policymakers to make sustainable, cost-effective decisions.
5. Reducing Government Administration Costs
Administrative tasks account for a significant portion of government spending, but AI-driven automation offers a path to reduce these costs.
Digital Document Management
AI-powered document processing systems can automate the classification, filing, and retrieval of government records. Optical character recognition (OCR) and NLP allow digital systems to process vast amounts of paperwork quickly, reducing costs associated with physical document storage and labor-intensive filing tasks.
Automated Customer Service
AI chatbots can handle basic citizen inquiries, reducing the need for call centers and administrative staff for routine queries. For example, implementing AI chatbots across government agencies could provide quick answers on tax filings, benefits eligibility, and passport renewals, ensuring more efficient use of human resources.
Predictive Maintenance of Public Infrastructure
AI can predict when infrastructure requires maintenance, allowing for proactive interventions that prevent costly repairs. In transportation, AI could monitor railway systems or road networks, identifying issues before they cause major disruptions. This predictive approach can reduce maintenance costs and increase the longevity of public assets.
Final Thoughts: A Future of Efficiency and Transparency
AI offers the UK government powerful tools to improve efficiency, combat fraud, and optimize spending. By adopting AI-driven systems, the government can cut down on unnecessary expenditures, ensure resources are allocated effectively, and reduce reliance on taxpayer funds to bridge budget gaps. However, to harness AI’s full potential, a robust regulatory framework must be established to ensure ethical use, protect privacy, and maintain transparency in government operations.
As the UK faces continued economic challenges, AI stands out as a crucial asset for achieving a leaner, more resilient public sector—one that can deliver better services to citizens without increasing the tax burden.
Trending AI News Articles
AI Questions and Answers section for Britain Cannot Tax & Spend Its Way Out of Its Economic Challenges
Welcome to a new feature where you can interact with our AI called Jeannie. You can ask her anything relating to this article. If this feature is available, you should see a small genie lamp above this text. Click on the lamp to start a chat or view the following questions that Jeannie has answered relating to Britain Cannot Tax & Spend Its Way Out of Its Economic Challenges.
Be the first to ask our Jeannie AI a question about this article
Look for the gold latern at the bottom right of your screen and click on it to enable Jeannie AI Chat.







