Type: Article -> Category: AI Healthcare

Exploring the Duality of AI
Balancing Human-Like Qualities and Logical Precision
Publish Date: Last Updated: 17th February 2026
Author: nick smith- With the help of CHATGPT
The question of whether we want AI to become more human is indeed complex and multifaceted. It largely depends on the specific goals we aim to achieve with artificial intelligence and the contexts in which we deploy it.
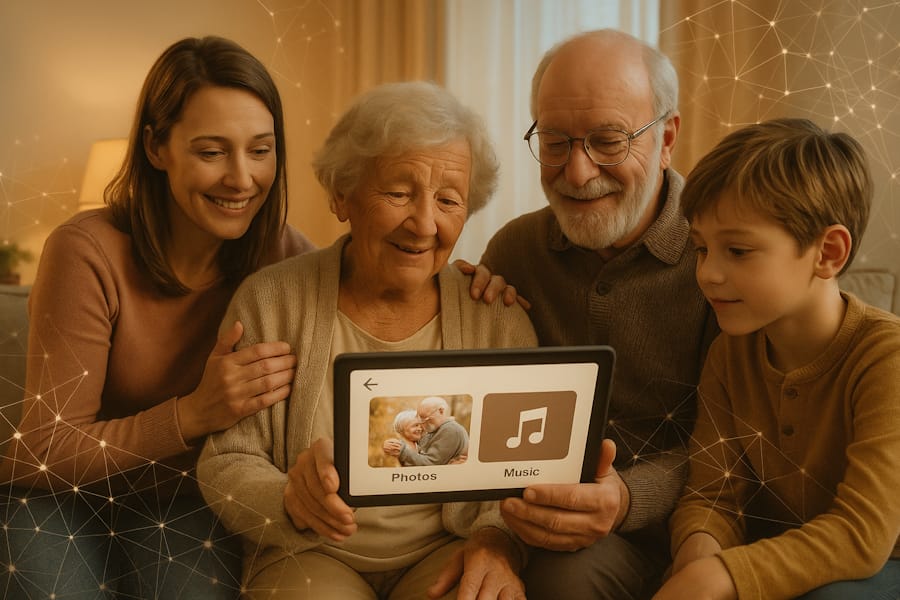
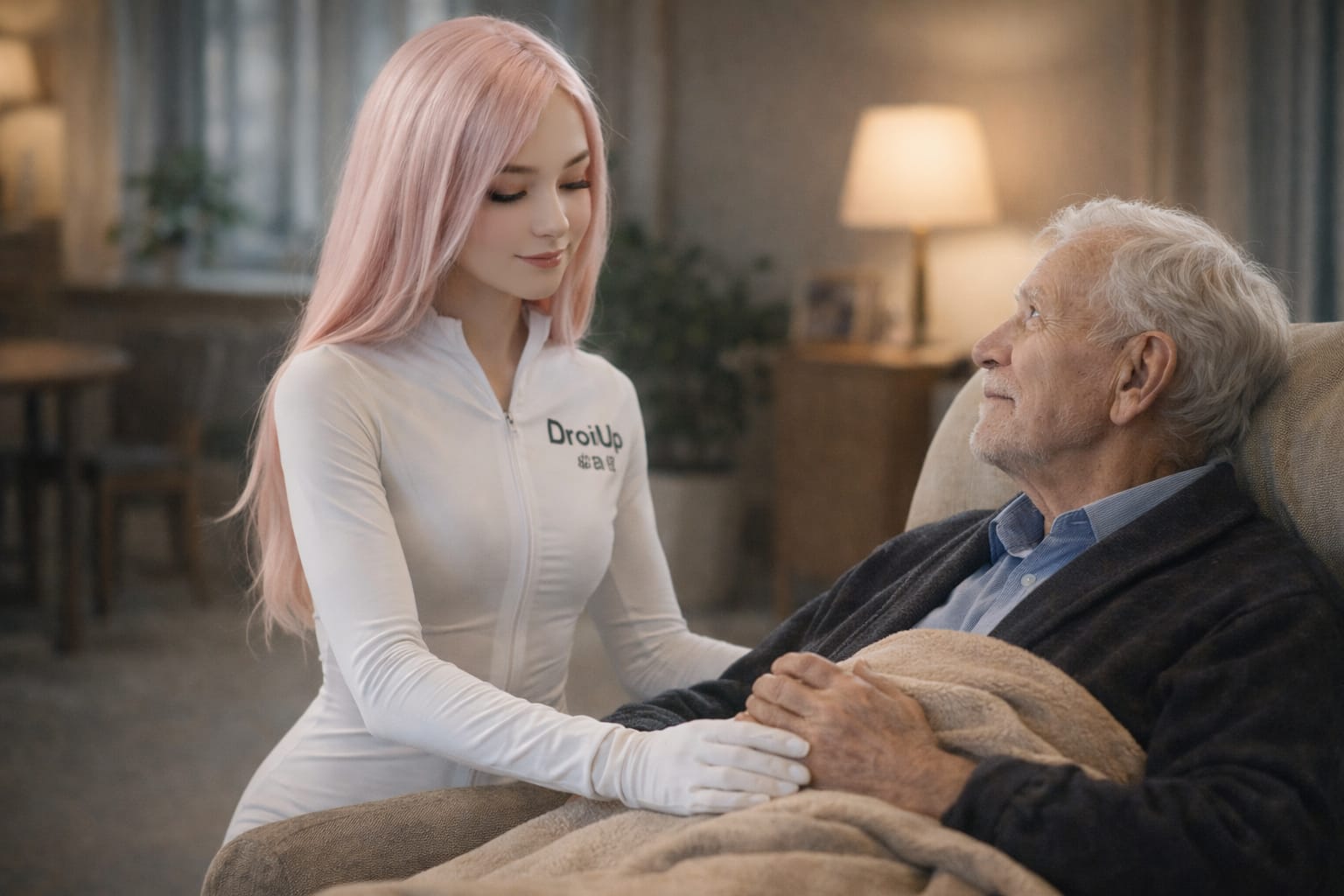
AI as a Companion for the Elderly

AI in Social Care Summit 2025: Ethical and Responsible Use of Generative AI
YouTube Channel: Institute for Ethics in AI Oxford

AI in Social Care Summit 2025: AI in Practice: How is it already being used and what’s coming next?
YouTube Channel: Institute for Ethics in AI Oxford
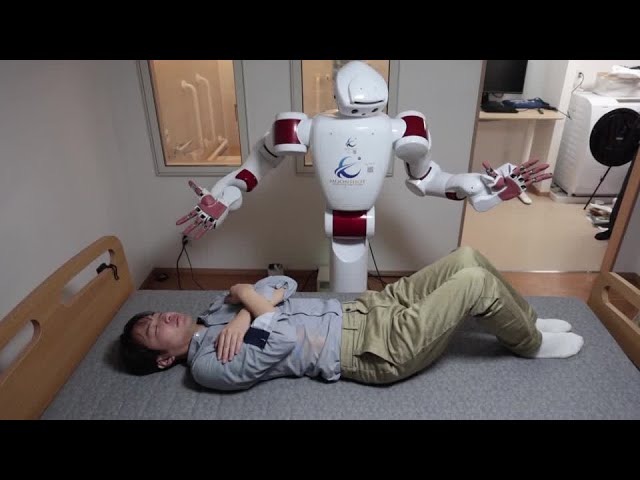

Aging Japan turns to AI robots to care for older people | REUTERS
YouTube Channel: Reuters

The Future of AI in Social Care Creating Sector Guidance part of Professional Care Workers' Week '24
YouTube Channel: The Care Workers' Charity
In many Western nations, the aging population faces significant challenges related to loneliness and social isolation. With some individuals spending up to 16 hours a day alone, AI has the potential to provide much-needed companionship. By developing AI that can emulate human-like interactions—displaying empathy, engaging in meaningful conversations, and understanding emotional cues—we could greatly enhance the quality of life for the elderly. Such AI companions could offer:
- Emotional Support: Providing comfort and reducing feelings of loneliness.
- Cognitive Engagement: Stimulating mental activity through games, discussions, and reminders.
- Assistance with Daily Tasks: Helping with medication schedules, appointments, and other routine activities.
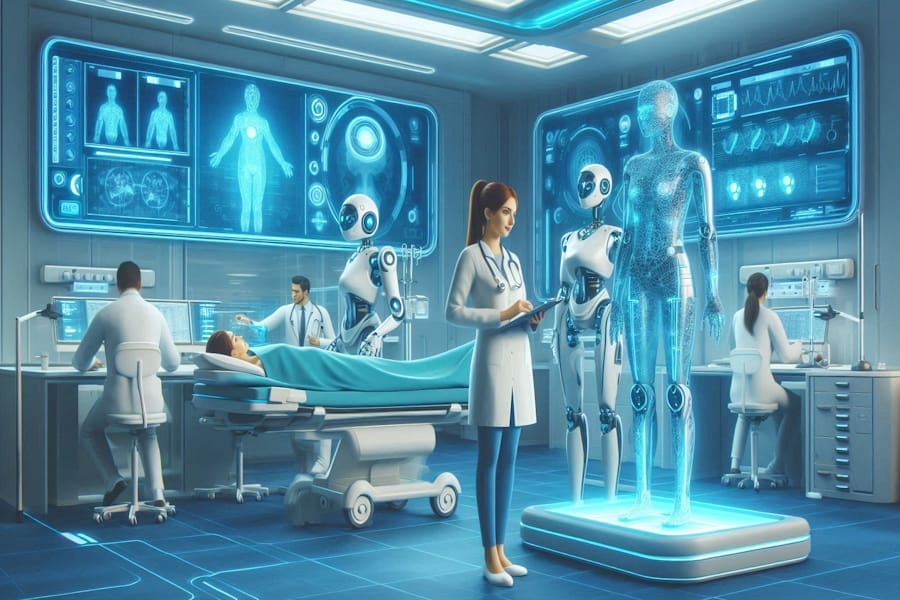
AI in Precision-Driven Fields
Conversely, there are areas where we prefer AI to operate without human-like emotions, relying instead on logical precision and data-driven decision-making. In fields such as medicine, finance, and engineering, the objective analysis provided by AI can lead to:
- Increased Efficiency: Processing vast amounts of data more quickly than humans.
- Reduced Errors: Eliminating mistakes caused by human fatigue or bias.
- Innovation: Identifying patterns and solutions that may not be immediately apparent to human experts.
The Yin and Yang of AI
This duality highlights why AI is both feared and appreciated. On one hand, AI offers unprecedented opportunities to improve lives, drive innovation, and solve complex problems. On the other hand, it poses risks related to misuse, ethical dilemmas, and unintended consequences. The "Yin and Yang" metaphor aptly captures this balance of potential benefits and downsides.
Challenges in Global Governance of AI
Given the current state of world politics, diverse governance models, and varying ethical standards, ensuring that AI is used responsibly is a significant challenge. Factors contributing to this difficulty include:
- Lack of Universal Regulations: There is no global consensus on AI ethics, leading to inconsistent standards.
- Bad Actors and Misuse: Organized crime and hostile entities may exploit AI for malicious purposes, such as cyberattacks, misinformation campaigns, or autonomous weapons.
- Technological Arms Race: Nations may prioritize strategic advantages over ethical considerations, especially in military applications.
AI in Warfare

The Rise of AI Warfare | The Watchtower Report
YouTube Channel: The Watchtower Report

The AI Arsenal That Could Stop World War III | Palmer Luckey | TED
YouTube Channel: TED

Helen Toner: OpenAI Reflections, Adaptation Buffers, and AI in Warfare
YouTube Channel: Cognitive Revolution "How AI Changes Everything"

"Fighting A Robot Army" – Navy SEALs REVEAL The Terrifying Truth About AI & The Future Of Global War
YouTube Channel: Valuetainment Short Clips
AI-driven warfare is already transforming the nature of conflict. Autonomous drones, intelligent surveillance systems, and cyber warfare capabilities are just a few examples of how AI is being integrated into military strategies. This raises several concerns:
- Escalation Risks: Autonomous systems may act unpredictably, potentially escalating conflicts without human oversight.
- Accountability: Determining responsibility for the actions of AI systems in warfare is legally and ethically complex.
- Arms Race Dynamics: Competition to develop advanced AI weapons can lead to global instability.
The Future: AI Versus AI
As AI technologies continue to advance, it's plausible that we will witness scenarios where AI systems are pitted against each other, reflecting the age-old human narrative of good versus evil. This could manifest in various ways:
- Cybersecurity: Defensive AI systems combating offensive AI-driven cyberattacks.
- Information Warfare: AI algorithms designed to detect and counteract misinformation generated by other AI.
- Military Conflicts: Autonomous weapons systems engaged in battles with minimal human intervention.
Navigating the Path Forward
To harness the positive potential of AI while mitigating its risks, a collective effort is required:
- Establish Ethical Frameworks: Develop international agreements that set clear ethical guidelines for AI development and use.
- Promote Transparency: Encourage open dialogue about AI capabilities and limitations to build public trust.
- Invest in AI for Good: Focus on applications of AI that address global challenges like healthcare, climate change, and education.
- Strengthen Regulations Against Misuse: Implement robust legal measures to deter and penalize unethical use of AI.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI mirrors the complexities of humanity itself. While we stand to gain immensely from AI that can enrich lives and advance society, we must remain vigilant about the ways in which it can be misused. By thoughtfully considering where we want AI to exhibit human-like qualities and where we prefer logical precision, we can better steer its development. Ultimately, the responsibility lies with us to guide AI in a direction that reflects our highest values and aspirations, ensuring it becomes a force for good rather than a catalyst for conflict.
Latest AI Healthcare Articles
AI Questions and Answers section for Exploring the Duality of AI: Balancing Human-Like Qualities and Logical Precision
Welcome to a new feature where you can interact with our AI called Jeannie. You can ask her anything relating to this article. If this feature is available, you should see a small genie lamp above this text. Click on the lamp to start a chat or view the following questions that Jeannie has answered relating to Exploring the Duality of AI: Balancing Human-Like Qualities and Logical Precision.
Be the first to ask our Jeannie AI a question about this article
Look for the gold latern at the bottom right of your screen and click on it to enable Jeannie AI Chat.
Type: Article -> Category: AI Healthcare