Type: Article -> Category: AI What Is
What is Deep Learning AI?
A Comprehensive Guide

Publish Date: Last Updated: 13th January 2026
Author: nick smith- With the help of GROK3
Deep Learning AI is a transformative subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that mimics the human brain’s neural networks to process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make intelligent decisions. By leveraging algorithms called neural networks, deep learning enables machines to learn from experience, improving their performance without explicit programming. This article explores the essence of deep learning AI, its history, current state, future potential, strengths, weaknesses, and real-world applications, answering the question: What is Deep Learning AI?
The History of Deep Learning AI
Deep learning AI traces its roots to the 1940s when researchers began modeling artificial neurons inspired by the human brain. The concept of neural networks emerged in 1943 with Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts’ mathematical model of neurons. In the 1950s, Frank Rosenblatt’s Perceptron, a single-layer neural network, laid the groundwork for modern deep learning.
However, early neural networks were limited by computational power and data availability. The 1980s saw advancements with backpropagation, an algorithm for training multi-layer neural networks, pioneered by Geoffrey Hinton and others. Despite this, deep learning remained niche due to hardware constraints and the popularity of simpler machine learning models.
The turning point came in the 2000s with the advent of powerful GPUs (graphics processing units), big data, and algorithmic breakthroughs. In 2012, AlexNet, a deep convolutional neural network, won the ImageNet competition, showcasing deep learning’s ability to outperform traditional methods in image recognition. This milestone sparked widespread adoption, cementing deep learning as a cornerstone of modern AI.
Where Deep Learning AI Stands Today
Today, deep learning AI powers many technologies we interact with daily. It underpins voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation systems on Netflix and YouTube, and advanced medical diagnostics. Companies like Google, Meta, and OpenAI continue to push boundaries with models like GPT, BERT, and DALL-E, which excel in natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and generative AI.
The democratization of deep learning tools, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud-based platforms, has made it accessible to businesses, researchers, and developers. However, challenges like high computational costs, ethical concerns, and the need for massive datasets persist.
The Future of Deep Learning AI
The future of deep learning AI is promising yet complex. Key trends include:
-
Efficient Models: Techniques like model pruning and quantization aim to create smaller, faster models for edge devices like smartphones and IoT systems.
-
Generalized AI: Researchers are working toward artificial general intelligence (AGI), where deep learning models can perform diverse tasks with human-like adaptability.
-
Ethical AI: Addressing biases, ensuring transparency, and regulating AI use will shape responsible development.
-
Interdisciplinary Applications: Deep learning will further integrate with fields like quantum computing, neuroscience, and robotics, unlocking new possibilities.
However, scaling deep learning to achieve these goals requires overcoming limitations like energy consumption and data dependency.
Strengths of Deep Learning AI
Deep learning AI offers several advantages:
-
Pattern Recognition: Excels at identifying complex patterns in images, text, and audio, surpassing traditional algorithms in tasks like object detection and speech recognition.
-
Automation: Reduces the need for manual feature engineering, as neural networks automatically learn relevant features from raw data.
-
Scalability: Performs better with more data and computational power, making it ideal for big data applications.
-
Versatility: Applicable across industries, from healthcare to finance to entertainment.
Weaknesses of Deep Learning AI
Despite its strengths, deep learning AI has notable limitations:
-
Data Hunger: Requires massive labeled datasets, which can be costly or unavailable.
-
Computational Cost: Training deep models demands significant hardware resources, leading to high energy consumption and environmental concerns.
-
Black Box Nature: Neural networks are often opaque, making it hard to interpret their decisions, a critical issue in fields like healthcare and law.
-
Overfitting Risk: Models may memorize training data instead of generalizing, leading to poor real-world performance.
-
Ethical Challenges: Biases in training data can perpetuate unfair outcomes, and misuse raises privacy and security concerns.
Real-World Applications of Deep Learning AI
Deep learning AI is transforming industries with practical applications:
-
Healthcare: Deep learning aids in early disease detection, such as identifying cancer in medical imaging (e.g., mammograms) or predicting patient outcomes using electronic health records.
-
Automotive: Self-driving cars rely on deep learning for object detection, lane detection, and path planning, as seen in Tesla’s Autopilot and Waymo’s autonomous vehicles.
-
Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and credit scoring benefit from deep learning’s ability to analyze complex patterns in transaction data.
-
Retail and E-commerce: Recommendation engines, personalized marketing, and inventory management use deep learning to enhance customer experiences and optimize operations.
-
Entertainment: Streaming platforms leverage deep learning for content recommendations, while generative AI creates art, music, and realistic deepfakes.
-
Natural Language Processing: Chatbots, translation tools (e.g., Google Translate), and sentiment analysis rely on deep learning models like transformers.
Conclusion
What is Deep Learning AI? It’s a powerful AI paradigm that uses neural networks to learn from data, driving innovations across industries. From its origins in the 1940s to its current dominance in AI, deep learning has revolutionized technology. Its future holds immense potential, but challenges like data requirements, interpretability, and ethics must be addressed. By understanding its strengths, weaknesses, and applications, we can harness deep learning AI to create a smarter, more responsible world.
For businesses and individuals looking to leverage deep learning AI, the key is to balance its capabilities with practical considerations, ensuring ethical and efficient use. As deep learning continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the future of artificial intelligence and human progress.
AI Deep Learning on YouTube

Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning | AI Fundamentals Course | 1.1
YouTube Channel: Tech Gee
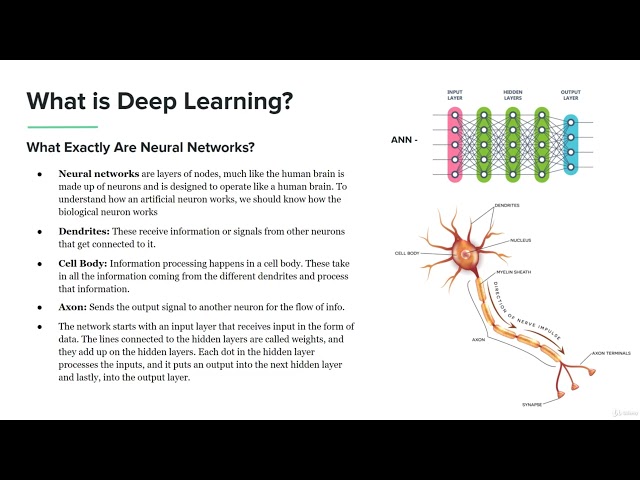
Lecture 5: What is Deep Learning? | Neural Networks Explained | Tech Lab – AI
YouTube Channel: Tech Lab

What are Deep Learning Architectures?
YouTube Channel: koombea

Episode 1: Deep Learning Explained from Scratch | Start Here!
YouTube Channel: Priya Bhatia
More great What Is? articles with AI
AI Questions and Answers section for What is Deep Learning AI?
Welcome to a new feature where you can interact with our AI called Jeannie. You can ask her anything relating to this article. If this feature is available, you should see a small genie lamp above this text. Click on the lamp to start a chat or view the following questions that Jeannie has answered relating to What is Deep Learning AI?.
Be the first to ask our Jeannie AI a question about this article
Look for the gold latern at the bottom right of your screen and click on it to enable Jeannie AI Chat.
Type: Article -> Category: AI What Is


